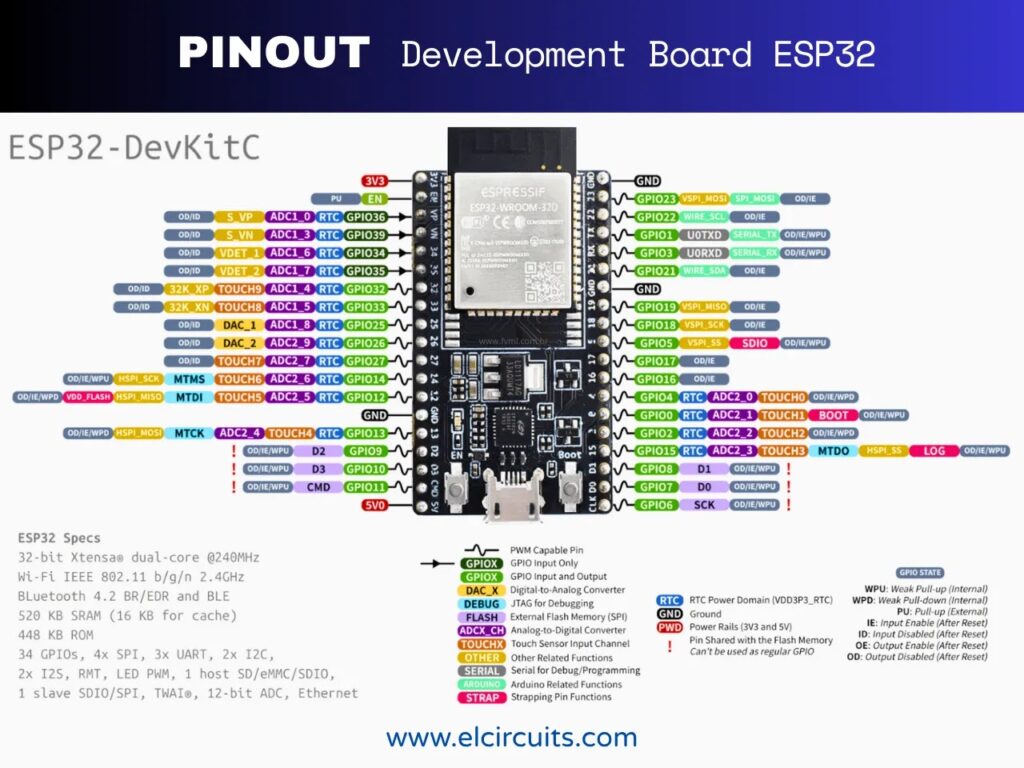
ESP8266 vs ESP32 vs Arduino: Which One to Choose for Your IoT Project?

Hello Tech Enthusiasts!
If you're starting an Internet of Things (IoT) project, you've probably faced the question: ESP8266, ESP32, or Arduino? All are excellent microcontrollers, but each has its own characteristics that can directly influence the success of your project. In this article, we'll compare the three in a clear and practical way, analyzing performance, connectivity, power consumption, and cost-effectiveness.
🔷 Understanding What Microcontrollers Are
The role of microcontrollers in IoT
Microcontrollers are the heart of smart devices. They collect data from sensors, process information, and send commands to other components, all in an automated way. Think of them as small brains that bring life to your electronic projects!
💡 Expert tip: For IoT projects, the ideal microcontroller should have integrated connectivity, low power consumption, and sufficient processing capacity to handle sensor data and network communication.
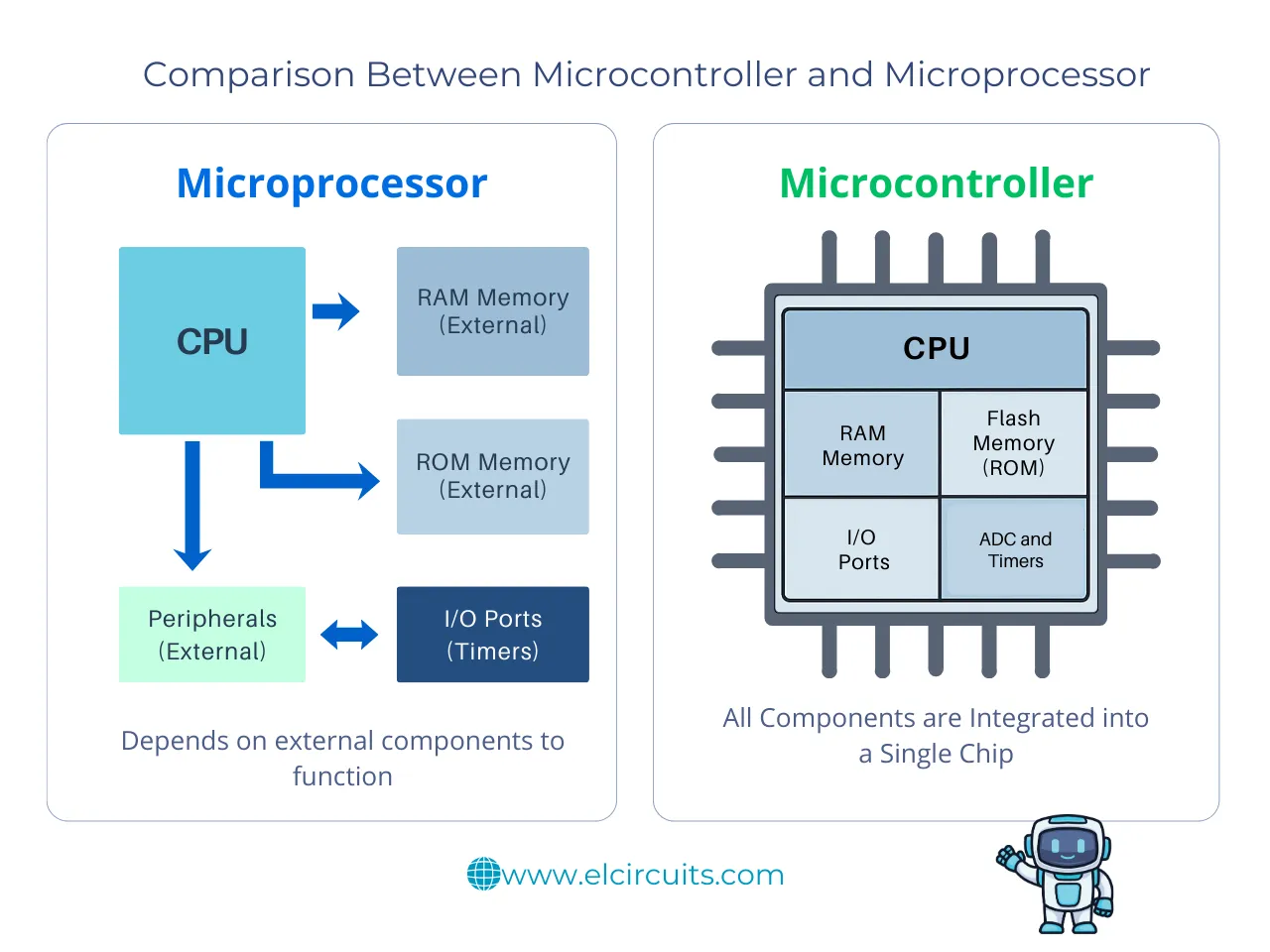
The Difference Between Microcontroller and Microprocessor
While microcontrollers have integrated memory and peripherals (like ADCs and GPIOs), microprocessors depend on external components. This is why microcontrollers are ideal for embedded and IoT projects.
🔅 Overview of Main Models
The Classic Arduino
Arduino is an open-source platform based on AVR microcontrollers (like the ATmega328P). It's widely used by beginners due to its simplicity and extensive support community. It's like the "popular car" of microcontrollers: reliable, easy to use, and with many "workshops" available to learn!
The Revolutionary ESP8266
Created by Espressif, the ESP8266 gained popularity for bringing integrated Wi-Fi at a very low cost, making it feasible to create connected devices without external modules. It was responsible for democratizing home IoT!
The Powerful ESP32
The ESP32 is a direct evolution of the ESP8266, bringing Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, greater processing, more pins, and low-power features, ideal for professional and industrial applications. Think of it as the "sports car" of microcontrollers: power, features, and versatility!
📊 Technical Comparison: ESP8266 vs ESP32 vs Arduino
| Feature | ESP8266 | ESP32 | Arduino Uno |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | 1 core (80–160 MHz) | Dual-core (240 MHz) | 1 core (16 MHz) |
| Connectivity | Wi-Fi | Wi-Fi + Bluetooth | None |
| RAM Memory | 160 KB | 520 KB | 2 KB |
| GPIOs | 17 | 36 | 14 |
| ADC | 10 bits | 12 bits | 10 bits |
| IoT Support | High | Very high | Low |
| Average Cost | R$ 25–35 | R$ 40–60 | R$ 60–90 |
📈 Quick Analysis: The ESP32 offers the best set of features for IoT, with dual connectivity, more memory, and superior processing. The ESP8266 remains an economical option for simpler projects, while Arduino is ideal for beginners and local projects.
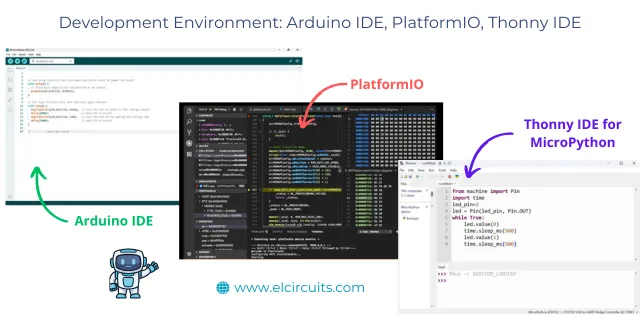
🧑💻 Programming Ease
Development environment
All can be programmed using the Arduino IDE, which simplifies the learning curve. The ESP32 and ESP8266 can also be programmed with MicroPython and PlatformIO, ideal for more advanced projects.
Supported languages
- Arduino: C/C++
- ESP8266/ESP32: C/C++, MicroPython, Lua, and even JavaScript (with specific firmware)
✅ Recommendation: If you already know the Arduino language, starting with ESP8266 or ESP32 using the same IDE will be a natural transition. For those who prefer Python, MicroPython on ESP32 is an excellent option!
🛜 Connectivity and Communication
Integrated Wi-Fi
This is the great advantage of the ESPs. While Arduino needs external modules (like the ESP-01 or Ethernet Shield), the ESP8266 and ESP32 come ready to connect to the internet.
Bluetooth on ESP32
The ESP32 stands out with Bluetooth Classic and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy), allowing integration with smartphones, sensors, and wearable devices.
⚡ Power Consumption
Battery-powered projects
The ESP32 has more advanced power-saving modes (like Deep Sleep), consuming only a few microamps. The ESP8266 also has this mode, but with less efficiency. The Arduino consumes more, making it less ideal for battery-powered devices.
🔋 Practical example: A temperature sensor with ESP32 in Deep Sleep mode can work for months on a single 3.7V battery, while a similar Arduino would need frequent replacements or a continuous power supply.
📎 Additional Features
ADC, PWM, and sensors
The ESP32 offers better ADC resolution (12 bits), more PWM channels, and native support for touch sensors and CAN communication.
Security and encryption
IoT projects require security. The ESP32 has AES, SHA, and RSA encryption embedded, something absent in Arduino and limited in ESP8266.
⚠️ Security alert: For IoT projects that handle sensitive data, the ESP32 offers much more robust security features, essential to protect against common vulnerabilities in connected devices.
💰 Cost-Effectiveness
The ESP8266 still reigns in terms of low cost with good performance. The ESP32 is slightly more expensive, but delivers many more features. Arduino, on the other hand, is great for learning, but costs more and offers less for connected IoT.
👀 When to Choose Arduino
Ideal for beginners
If you've never programmed a microcontroller, Arduino is the perfect starting point. Its vast community and simplicity dramatically reduce entry barriers.
Simple and educational projects
For local automations or prototypes that don't require internet, Arduino is still an excellent choice.
🎓 Ideal educational projects for Arduino:
- Basic robotics
- LED and motor control
- Proximity and temperature sensors
- Small games and displays
🤷♂️ When to Choose ESP8266
For those seeking cheap Wi-Fi
The ESP8266 is the perfect choice if you want to connect sensors or devices to the cloud without spending much.
Typical applications
- Wi-Fi thermometers
- Smart plugs
- Remote monitoring via MQTT
💡 Success case: A smart irrigation system that monitors soil moisture and controls valves remotely can be implemented with ESP8266 at a very low cost, sending data to an application via Wi-Fi.
🤔 When to Choose ESP32
More robust projects
If you need performance, Bluetooth connectivity, and multiple peripherals, the ESP32 is unbeatable.
Typical applications
- Home automation
- Smart robots
- Wearable devices
- IoT gateways
🚀 Advanced project: A personal voice assistant with touchscreen display, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, and device control by voice commands is perfectly feasible with a single ESP32, thanks to its dual-core processing power and multiple interfaces.
🧩 Compatibility with Sensors and Modules
Both ESP8266 and ESP32 are compatible with most sensors used in Arduino (DHT11, BMP280, HC-SR04, etc.), making migration simple.
🎯 Which Is Best to Start in IoT?
If the focus is on learning the basics, start with Arduino Uno. But if the goal is to create real connected devices, the ESP8266 or ESP32 are clearly superior.
🧾 Conclusion: The Right Choice Depends on Your Project
There is no single answer.
- Want something simple and educational? Go with Arduino.
- Need cheap Wi-Fi? Choose the ESP8266.
- Looking for power and flexibility? The ESP32 is the ideal path.
In summary: the ESP8266 popularized home IoT, the ESP32 professionalized it, and Arduino continues to be the gateway for all who want to learn electronics in a fun way.
🤔 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
To ensure your project is a success, we've compiled some of the most common questions about this charger. Check it out!
Can I use Arduino sensors on ESP8266 or ESP32? 🔽
Yes! Most sensors compatible with Arduino (like DHT11, BMP280, HC-SR04, etc.) work perfectly on ESPs. You may need to adjust libraries or pins, but the hardware is compatible.
Which consumes less battery? 🔽
The ESP32 has the most efficient power-saving modes, especially Deep Sleep mode. For battery-powered projects, the ESP32 is generally the best choice.
Is it difficult to migrate from Arduino to ESP? 🔽
No! You can program the ESPs using the same Arduino IDE and C/C++ language. The transition is quite natural, especially if you're already familiar with Arduino programming.
Can I use Arduino and ESP together in the same project? 🔽
Yes! Many projects use Arduino for local control and an ESP8266 as a Wi-Fi module. The ESP32 can also be used as a main processor or co-processor in more complex projects.
Which is best for an IoT beginner? 🔽
If you already have experience with Arduino, the ESP8266 is an excellent next step to add Wi-Fi connectivity to your projects. If you're starting from scratch, it might be better to learn the basics with Arduino first.
🎯 Did You Like This Article?
Leave your comment below with your questions or experiences with these microcontrollers!
✨ Our Gratitude and Next Steps
We sincerely hope this guide has been useful and enriching for your projects! Thank you for dedicating your time to this content.
Your Feedback is Invaluable:
Have any questions, suggestions, or corrections? Feel free to share them in the comments below! Your contribution helps us refine this content for the entire ElCircuits community.
If you found this guide helpful, spread the knowledge!
🔗 Share This GuideBest regards,
The ElCircuits Team ⚡
 Português
Português Español
Español