Types of Arduino: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Board
Arduino was born at the Interaction Design Institute in Ivrea with a simple goal: to allow students without experience in electronics and programming to create interactive projects. What started as an educational tool evolved to become one of the most versatile platforms in the maker world, adapting to new requirements and technological challenges.
Today, Arduino boards range from simple 8-bit versions to advanced products for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, 3D printing, wearables, and embedded environments. This diversity allows both beginners and professionals to find the perfect board for their projects.
One of the greatest virtues of the Arduino ecosystem is that all boards are fully open-source, allowing users to create them independently and adapt them to their specific needs. This open philosophy has driven a global community of creators who share knowledge and continuously expand the possibilities of these boards.
💡 Curiosity: Over the years, Arduino boards have been used to build thousands of projects, from everyday objects to complex scientific instruments. An international community of designers, artists, students, programmers, and enthusiasts has formed around this platform, contributing an impressive amount of knowledge accessible to all.
What is Arduino?
The Arduino board is an open-source platform used to develop electronic projects. It consists of two main components:
🔧 Hardware
A physical board with a microcontroller that can be programmed to interact with sensors, motors, LEDs, and other electronic components.
💻 Software
The Integrated Development Environment (IDE) that runs on your computer, allowing you to write and upload code to the physical board.
👉 To better understand what Arduino is: Arduino: What It Is, How It Works, and Why You Should Start Using It!
Why choose Arduino boards?
Arduino boards have become popular for various reasons, especially for their accessibility and versatility. The Arduino software is extremely beginner-friendly, yet flexible enough for advanced users.
The IDE is available for free on Windows, Linux, and Mac, facilitating its use in educational environments. Teachers and students can use it to create low-cost scientific instruments and demonstrate physics and chemistry principles practically.
Although there are other microcontroller platforms like Netmedia's BX-24, the Parallax Basic Stamp, MIT's Handyboard, and Phidget, Arduino offers distinctive advantages:
- ✅ Affordable: Accessible boards for all budgets
- ✅ Cross-platform: Works on Windows, Mac, and Linux
- ✅ Simple programming environment: Clean and intuitive interface
- ✅ Open-Source Software: Fully customizable and extensible
- ✅ Open hardware: Schematics and designs available for modification
Types of Arduino Boards
Every day, new types of embedded boards emerge worldwide, with differentiated functionalities and improved designs that make usability increasingly better. There are numerous varieties of Arduino boards, but we will focus on the most popular and easiest to find in the Brazilian market.
📌 Note: This guide covers the most popular boards in Brazil. If you are looking for newer models like the Arduino Portenta or the Nano 33 BLE, leave a comment at the end of the article and we can address them in future publications!
The most commonly used Arduino board:
Arduino UNO
- The most popular board for beginners
Arduino Mega
- For complex projects with many components
Arduino Nano
- Compact and perfect for small prototypes
Arduino Pro Mini
- Ultra compact for final projects
Arduino Leonardo
- With native USB communication
Arduino LilyPad
- Designed for wearables and smart clothing
Detailed Analysis of Main Arduino Boards
1. Arduino Uno R3: The Classic for Beginners
🏆 Ideal for: Beginners, educational projects, and simple prototypes
Microcontroller: ATmega328P | Clock: 16 MHz
Advantages:
- ✔️ Integrated USB communication (plug-and-play)
- ✔️ Compatible with 90% of Shields (expansions)
- ✔️ Ideal for educational projects (e.g., traffic light, alarm)
- ✔️ Widely documented with thousands of tutorials
- ✔️ Large online support community
Disadvantages:
- ❌ Limited memory for systems with many sensors
- ❌ Fewer I/O pins compared to larger models
💰 Average price in the USA: $15 - $30
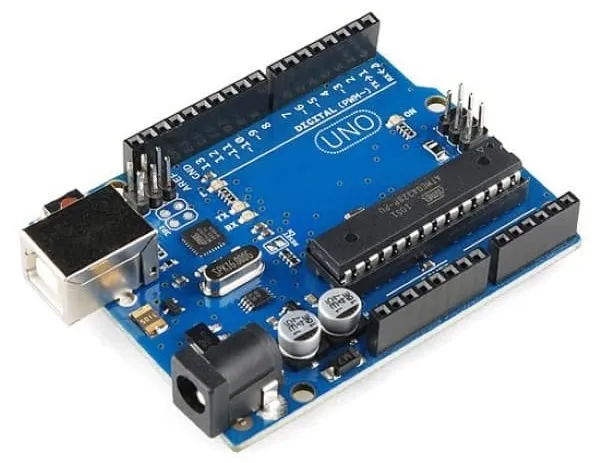
Arduino Uno R3 Specifications
💡 Ideal Project for Arduino Uno:
The Arduino Uno is perfect for creating an automated irrigation system for plants. With its 6 analog pins, you can monitor soil moisture in different pots and activate water pumps when necessary. It is an excellent educational project that teaches electronics, programming, and automation concepts!
2. Arduino Mega R3: Power for Complex Systems
🏆 Ideal for: Industrial automation, advanced robotics, and projects with multiple sensors
Microcontroller: ATmega2560 | Clock: 16 MHz
Highlight: 54 I/O pins and 256KB of memory.
Best For:
- ✔️ Industrial automation
- ✔️ Systems with multiple sensors (e.g., smart greenhouse)
- ✔️ Complex robotics projects
- ✔️ CNC controllers and 3D printers
Comparison:
- Mega vs. Uno: 4x more memory, but 2x more expensive
- Mega vs. Nano: Significantly larger, but with many more pins
💰 Average price in the USA: $15 - $45
⚠️ Caution: Requires a 12V power supply to function with all peripherals.
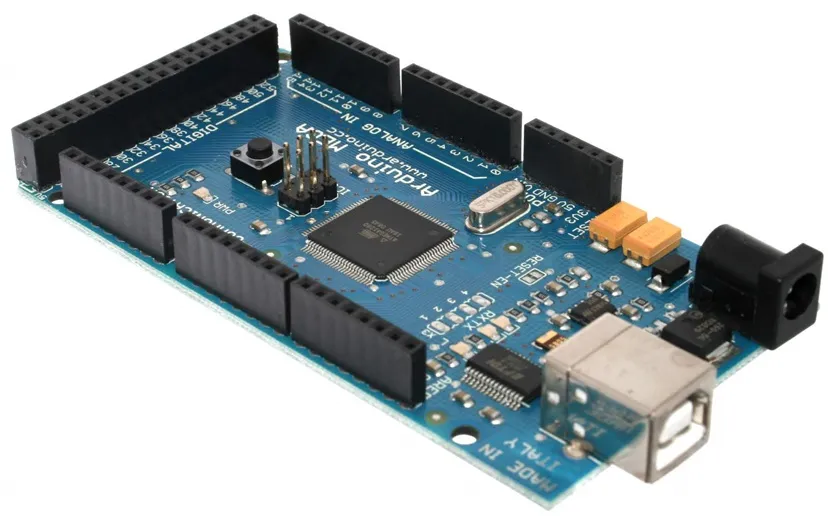
Arduino Mega (R3) Specifications
💡 Ideal Project for Arduino Mega:
With its 54 digital pins and 16 analog inputs, the Arduino Mega is perfect for building a complete smart greenhouse. You can monitor temperature, humidity, light, soil pH, control irrigation systems, lighting, ventilation, and still have pins left for future expansions!
3. Arduino Nano: Compact and Versatile
🏆 Ideal for: Compact projects, breadboard prototypes, and wearables
Microcontroller: ATmega328 | Clock: 16 MHz
Advantages:
- ✔️ 45% smaller than the Uno
- ✔️ USB-C in recent versions (Nano Every)
- ✔️ Perfect for breadboards (fits directly)
- ✔️ Low power consumption
Uses:
Drones, Wearables, battery-powered projects, compact prototypes.
Common Mistake:
- ❌ Do not use in projects with more than 8 sensors (lack of pins)
💰 Average price in the USA: $5 - $25

Arduino Nano 3.0 Specifications
💡 Ideal Project for Arduino Nano:
The Arduino Nano is perfect for creating a mini quadcopter drone. Its compact size and reduced weight are ideal for aerial applications, while its PWM pins allow precise control of the four motors. Add an MPU-6050 sensor for stabilization and you'll have a functional drone in a small space!
4. Arduino Pro Mini: Compact and Pure for Professional Projects
🏆 Ideal for: Final projects where space and economy are essential
Microcontroller: ATmega328P | Clock: 16 MHz
Advantages:
- ✔️ Dimensions: 18mm x 33mm (60% smaller than the Uno)
- ✔️ Extremely low cost
- ✔️ Energy efficiency, with minimal consumption
- ✔️ Perfect for projects that will be permanently assembled
Disadvantages:
- ❌ No Integrated USB: Requires FTDI adapter or USB-Serial converter for programming
- ❌ No Voltage Regulator: Power supply must be stable (e.g., exact 3.3V or 5V)
💰 Average price in the USA: $5 - $15
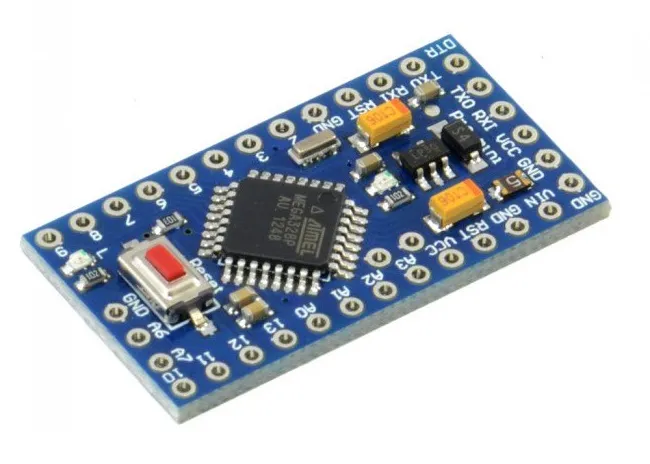

Arduino Pro Mini Specifications
💡 Ideal Project for Arduino Pro Mini:
The Pro Mini is excellent for creating a beehive monitoring system. Its reduced size allows for discreet installation inside the hive, and its low power consumption ensures long battery life. With temperature, humidity, and weight sensors, you can monitor the health of the hive remotely!
5. Arduino Leonardo: The Board with Integrated USB Communication
🏆 Ideal for: Projects that need to interact directly with the computer
Microcontroller: ATmega32u4 (with native USB) | Clock: 16 MHz
Advantages:
- ✔️ Native USB communication (Can emulate keyboards, mice, and controllers (HID))
- ✔️ Automation projects (e.g., custom macro keyboard)
- ✔️ Direct interaction with PC without extra components
- ✔️ More digital pins than the Uno (20 vs 14)
Disadvantages:
-
❌
ompatibility: Some Shields do not work due to the difference in the USB chip - ❌ Learning Curve: Requires care when programming HID functions
Comparison:
- Leonardo vs. Uno: 6 extra digital pins and 6 additional analog inputs
💰 Average price in the USA: $10 - $25

Arduino Leonardo Specifications
💡 Ideal Project for Arduino Leonardo:
With its ability to emulate USB devices, the Leonardo is perfect for creating a custom controller for games or editing software. You can build a joystick with programmable buttons, a dial to control parameters in audio or video software, or even a custom shortcut keyboard for your workflow!
6. Arduino LilyPad: Wearable Technology
🏆 Ideal for: Smart clothing projects and wearables
Differential: Circular shape and washable.
Applications:
- ✔️ Smart clothing (e.g., LED jacket)
- ✔️ Accessories with motion sensors
- ✔️ Interactive wearable art
- ✔️ Monitoring of vital signs in sportswear
Limitation:
- ❌ Does not support traditional Shields
💰 Average price in the USA: $10 - $30
🔧 Pro Tip: Use conductive thread to sew circuits!
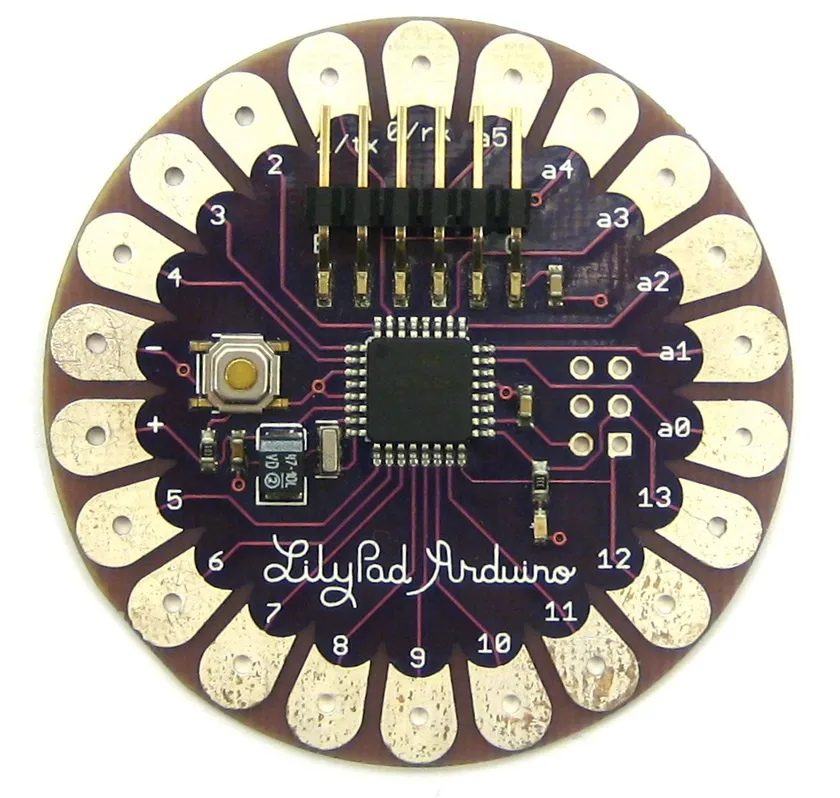
Arduino LilyPad Specifications
This Arduino technology was designed and developed by Leah Buechley and each LilyPad was created with large connectors to allow them to be sewn into clothing. There are various input, output, and sensor boards available, and all are washable.
💡 Ideal Project for Arduino LilyPad:
Create a smart cyclist jacket with the LilyPad! Add LEDs on the back that blink when you brake, directional arrows activated by buttons on the handlebars, and a light sensor that automatically increases the LED brightness at night. It's a practical, safe, and impressive project that demonstrates the full potential of wearables!
📖 Arduino Boards Comparative Table
In this table, we compare the main characteristics of Arduino boards to help you choose the ideal one for your project:
| Model | Microcontroller | Clock | Flash Memory | SRAM | EEPROM | Digital Pins | Analog Pins | Operating Voltage | Average Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino UNO | ATmega328P | 16 MHz | 32 KB | 2 KB | 1 KB | 14 (6 PWM) | 6 | 5V | $15 - $30 |
| Arduino Mega | ATmega2560 | 16 MHz | 256 KB | 8 KB | 4 KB | 54 (14 PWM) | 16 | 5V | $15 - $45 |
| Arduino Nano | ATmega328 | 16 MHz | 16 KB | 2 KB | 1 KB | 14 (6 PWM) | 8 | 5V | $5 - $25 |
| Arduino Pro Mini | ATmega328P | 8/16 MHz | 32 KB | 1 KB | 1 KB | 14 (6 PWM) | 8 | 3.3V/5V | $5 - $15 |
| Arduino Leonardo | ATmega32u4 | 16 MHz | 32 KB | 2.5 KB | 1 KB | 20 (7 PWM) | 12 | 5V | $10 - $25 |
| Arduino LilyPad | ATmega168V | 8 MHz | 16 KB | 1 KB | 512 B | 14 (6 PWM) | 6 | 2.7-5.5V | $10 - $30 |
💡 Tip: To quickly compare boards, note that the Arduino Mega offers 4x more flash memory than the UNO, while the Nano maintains the same specifications as the UNO in a 45% smaller format. The Pro Mini is ideal for final projects due to its reduced size and low consumption.
⚠️ Note on prices: The values presented are market averages in the USA and may vary according to the store and whether the product is an original board or a clone. Original Arduinos usually cost more but offer greater quality assurance and compatibility.
🎯 How to Choose the Ideal Arduino for Your Project?
For Beginners:
We recommend the Arduino Uno - it is the most documented board, with a vast support community and compatible with most available shields and tutorials.
For Compact Projects:
The Arduino Nano is ideal for breadboard prototypes or projects with limited space, maintaining the ease of programming of the Uno.
For Complex Projects:
If you need many pins or more memory, the Arduino Mega offers 54 digital pins and 256KB of flash memory.
For Final Projects:
The Arduino Pro Mini is perfect for projects that will be permanently assembled, due to its reduced size and low cost.
For Computer Interaction:
The Arduino Leonardo can emulate a keyboard and mouse, being ideal for custom controls and PC task automation.
For Wearables:
The Arduino LilyPad was specifically designed to be sewn into clothes and accessories, being washable and with a circular shape.
🤔 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
To ensure your project is a success, we have compiled some of the most common questions about this charger. Check it out!
What is the difference between Original Arduino and Clones? 🔽
Original Arduinos are manufactured by the official company and guarantee quality and support. Clones are cheaper versions produced by third parties, generally in China. Although they work similarly, they may have differences in component quality and reliability.
Can I use the same code on different Arduino boards? 🔽
In most cases, yes! Code written for an Arduino Uno will generally work on a Nano or Mega without modifications. However, if you are using specific pins or special features of a board, you may need to adjust the code.
Which is the best Arduino for beginners? 🔽
The Arduino Uno is generally recommended for beginners due to its simplicity, extensive documentation, and compatibility with most projects and tutorials available online.
Is Arduino difficult to learn? 🔽
No! Arduino was specifically designed to be accessible to beginners. The programming language is based on C/C++, but simplified, and there are thousands of tutorials, examples, and an active community to help you get started.
Can I power my Arduino directly through the USB port? 🔽
Yes! Most Arduino boards can be powered through the USB port, which provides 5V. However, for projects that consume more energy (like motors or many LEDs), it is recommended to use an external power supply.
💬 Share Your Experience!
Which Arduino do you use or intend to use?
Leave a comment below sharing your projects, questions, or experiences with different Arduino boards!
👋 Conclusion
We hope this complete guide on types of Arduino has helped you understand the differences between the main boards and choose the ideal one for your project. Remember that the Arduino ecosystem is vast and constantly evolving, so keep exploring and learning!
Thank you for visiting our blog, and we hope to see you again soon. Don't forget to check out our other content on technology and various topics.
✨ Our Gratitude and Next Steps
We sincerely hope this guide has been useful and enriching for your projects! Thank you for dedicating your time to this content.
Your Feedback is Invaluable:
Have any questions, suggestions, or corrections? Feel free to share them in the comments below! Your contribution helps us refine this content for the entire ElCircuits community.
If you found this guide helpful, share the knowledge!
🔗 Share This GuideBest regards,
The ElCircuits Team ⚡
 Português
Português Español
Español