DIY Audio Cables: Build Guitar, Keyboard & Mixer Cables Step-by-Step

DIY Audio Cables: Build Your Own Guitar, Keyboard, and Mixer Cables Step by Step – elcricuits.com
Hello, electronics enthusiasts!
Have you ever had trouble with incompatible audio cables or paid a lot for equipment you could have assembled yourself? In this complete guide you’ll learn how to make your own professional audio cables for mixers, microphones, musical instruments, church sound systems, studios and more.
🛠️ Ready to Get Hands-On?
We’ll start with the most common, essential cables used daily by musicians and audio techs. After that we’ll move on to more specific and complex options.
1. 1/4″ TS (Mono) — 1/4″ TS (Mono) — For Instruments
The 1/4″ TS (Tip-Sleeve) mono cable is one of the most used connectors in audio. It has two contacts (tip and sleeve) and is unbalanced. Its primary use is to connect instruments such as guitar, bass and keyboard to a mixer, amp or audio interface.
In live and recording contexts, this cable carries the instrument signal to the main sound system (PA — Public Address).
Figure 1 — 1/4″ TS (mono) Male → 1/4″ TS (mono) Male

Fig. 1 – 1/4″ TS (mono) male → 1/4″ TS (mono) male
💡 Practical tip: Use good-quality 1/4″ connectors and solid solder joints to avoid unwanted noise. Build your instrument cable with firm plugs and quality wire to prevent crackle and signal loss.
2. 1/4″ TRS (Stereo/Balanced) → 2× 1/4″ TS — Mixer Inserts
The 1/4″ TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) has three contacts and can be used as a balanced connection or to carry two separate mono signals.
On mixing consoles, TRS → dual TS cables are commonly used for insert connections, which send a channel’s signal to an external processor (compressor, EQ, effects) and return to the same channel.
Figure 2 — 1/4″ TRS → 2× 1/4″ TS
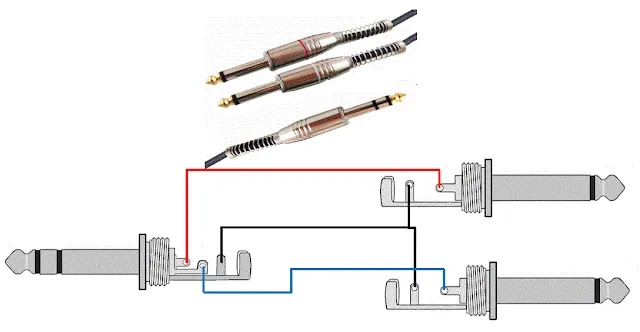
Fig. 2 – 1/4″ TRS → 2× 1/4″ TS
💡 Practical tip: Mark send and return plugs with labels or colored heat-shrink to avoid swapping them during live shows.
3. XLR Female → 2× 1/4″ TS — Converting Balanced Outputs
An XLR female to two 1/4″ TS cable allows equipment with a balanced output (mixers, interfaces) to feed unbalanced inputs (amps, speakers).
XLR pinout:
- Pin 1 = Ground (shield)
- Pin 2 = Positive (hot)
- Pin 3 = Negative (cold)
This cable splits a balanced signal into two independent mono channels.
Figure 3 — XLR female → 2× 1/4″ TS
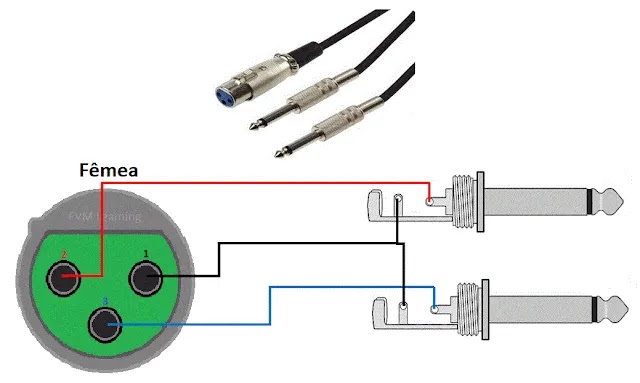
Fig. 3 – XLR female → 2× 1/4″ TS
💡 Practical tip: Use this cable only when necessary. Whenever possible keep balanced-to-balanced (XLR ↔ XLR or TRS ↔ XLR) connections to reduce noise and interference, especially over long cable runs.
4. XLR Female → 1/4″ TS — Balanced to Unbalanced Adapter
This adapter is commonly used to connect balanced outputs (XLR) to unbalanced inputs (1/4″ TS) — for example:
- Connecting a professional microphone to a mixer or amplifier that only has a 1/4″ input (common in simpler gear).
- Feeding a balanced mixer/interface output to an amplifier or active speaker with a 1/4″ TS input.
This connection adapts a 3-wire balanced signal to 2-wire unbalanced by discarding or tying the negative conductor (XLR pin 3) to ground, using only the positive (pin 2) and shield (pin 1) to the tip and sleeve of TS plug.
Figure 4 — XLR female → 1/4″ TS
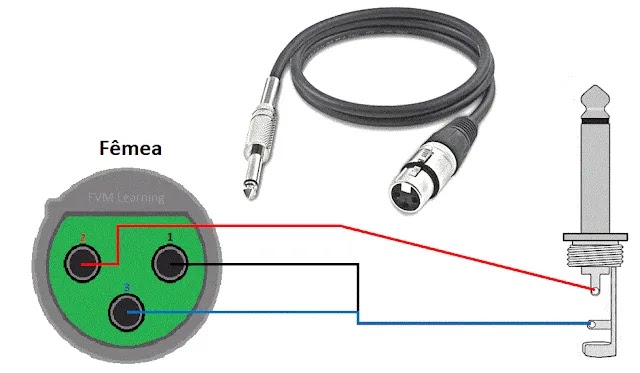
Fig. 4 – XLR female → 1/4″ TS
💡 Practical tip: Before connecting cables to equipment that provides phantom power, confirm the connected device supports it. This helps avoid damaging dynamic microphones or certain instruments.
5. XLR Male → 2× 1/4″ TS — Splitting a Balanced Signal
This cable splits a balanced XLR male signal into two unbalanced 1/4″ TS outputs (one per TS connector).
Practically it works as a splitter: sending the positive (pin 2) to one TS and the negative (pin 3) to the other. Use carefully because it does not replace a true stereo output and can introduce phase issues.
Figure 5 — XLR Male → 2× 1/4″ TS
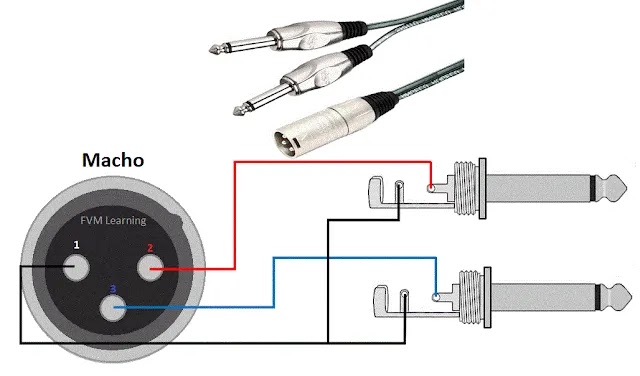
Fig. 5 – XLR male → 2× 1/4″ TS
💡 Practical tip: Useful for recording or testing but be mindful of phase and level issues — splitting like this is not a substitute for a true stereo source.
6. XLR Male → 1/4″ TS — Balanced XLR to TRS
This cable maps XLR male balanced pins to a 1/4″ TS balanced input: pin 2 → tip, pin 3 → ring, pin 1 → sleeve. It’s commonly used to connect balanced outputs to TRS inputs (for example, direct boxes and many interfaces).
Figure 6 — XLR Male → 1/4″ TRS

Fig. 6 – XLR male → 1/4″ TS
💡 Practical tip: Use this cable only when necessary. Whenever possible keep balanced-to-balanced (XLR ↔ XLR or TRS ↔ XLR) connections to reduce noise and interference, especially over long cable runs.
7. XLR Male → 1/4″ TS — Mixer/Interface to Amps or Speakers
The XLR male to 1/4″ TS cable converts a balanced XLR output to an unbalanced TS input — used for amplifiers, active speakers and some instruments. Avoid long runs with this type of cable because you lose the benefits of a balanced line.
Figure 7 — XLR Male → 1/4″ TS
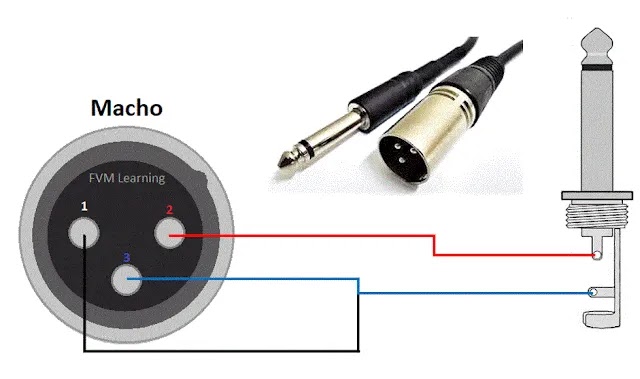
Fig. 7 – XLR male → 1/4″ TS
💡 Practical tip: Avoid long lengths in this configuration — the loss of balanced wiring can introduce noise.
8. XLR Female ↔ XLR Male — Balanced Microphone Cables
This is the classic microphone cable, used for balanced extensions and for connecting peripherals like active speakers, amplifiers, EQs and effects to the audio console.
Because it uses three conductors (ground, positive and negative), the XLR cable provides protection from noise and can be run much longer than unbalanced cables.
Figure 8 — XLR Female → XLR Male

Fig. 8 – XLR female → XLR male
💡 Practical tip: Invest in quality XLR cables if you plan to use condenser microphones or run long cable lengths.
9. XLR Female → 1/4″ TS — Players, Mixers and DJ Gear
This cable converts two RCA signals (left and right) into one 1/4″ TRS stereo plug. It is often used with DJ mixers, media players and receivers to feed a mixer or interface TRS input.
Figure 9 — XLR Female → 1/4″ TS
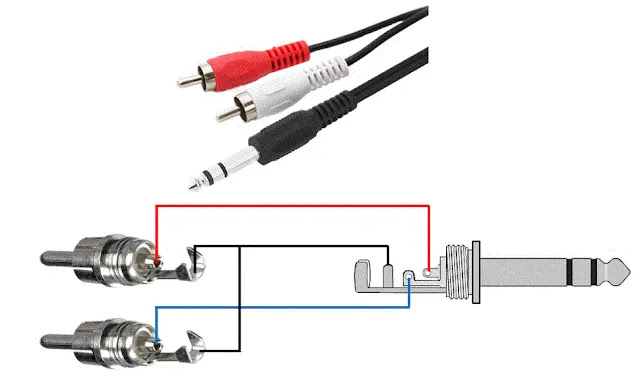
Fig. 9 – XLR female → 1/4″ TS
💡 Practical tip: Keep RCA runs short to reduce interference.
10. 2× RCA → 1/4″ TS — Split RCA to Two Mono TS
Here each RCA output (L/R) is wired individually to a TS plug. Useful in hybrid setups when connecting consumer audio sources (CD/DVD/players) to an audio system or active speakers with 1/4″ inputs.
Figure 10 — 2× RCA → 1/4″ TS

Fig. 10 – 2× RCA → 1/4″ TS
💡 Practical tip: Verify channel mapping (red = right, white = left).
11. 2× RCA → 1/4″ TS — Standard Stereo RCA
Standard stereo RCA cables are very common for home audio gear (CD, DVD, turntables, receivers) and some older mixers. They carry unbalanced left and right channels.
Figure 11 — 2× RCA → 1/4″ TS
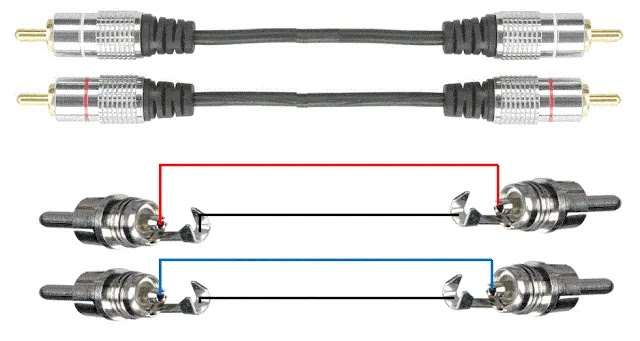
Fig. 11 – 2× RCA → 1/4″ TS
💡 Practical tip: Ideal for short distances only — for professional setups prefer balanced connections whenever possible.
📋 Summary Table — Common Audio Cable Types
Below are the main cables covered in this guide, their uses and quick tips.
| Nº | Cable | Connectors | Main Use | Signal Type | Quick Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/4″ TS → 1/4″ TS | 2× 1/4″ TS (male) | Guitar, bass, keyboard | Unbalanced | Use short runs to avoid noise. |
| 2 | 1/4″ TRS → 2× 1/4″ TS | 1× TRS → 2× TS | Insert / stereo split | Unbalanced (or balanced if used as TRS) | Good for headphone outs and keyboard stereo splits. |
| 3 | 1/4″ TRS → 1/4″ TRS | 2× TRS | Headphones, stereo outputs | Unbalanced / Balanced | Avoid lengths over ~3 m for unbalanced signals. |
| 4 | XLR (F) → 1/4″ TRS | XLR F → TRS | Mic or balanced out to TRS | Balanced | Maintains quality over long runs. |
| 5 | XLR (F) → 1/4″ TS | XLR F → TS | Adapt XLR to TS input | Unbalanced | Use only when no balanced input is available. |
| 6 | XLR (M) → 2× 1/4″ TS | XLR M → 2× TS | Split balanced to two TS | Semi-balanced | For tests only; watch for phase issues. |
| 7 | XLR (M) → 1/4″ TRS | XLR M → TRS | Mic/mixer to TRS input | Balanced | Common in studios & interfaces. |
| 8 | XLR (M) → 1/4″ TS | XLR M → TS | Mixer/interface to amp/speaker | Unbalanced | Prefer short runs. |
| 9 | XLR F → XLR M | XLR F ↔ XLR M | Microphone cables, extensions | Balanced | Professional standard; long distances OK. |
| 10 | 2× RCA → 1/4″ TRS | 2× RCA → TRS | DJ gear, players, domestic mixers | Unbalanced | Keep RCA runs short to avoid noise. |
| 11 | 2× RCA → 2× 1/4″ TS | 2× RCA → 2× TS | Adapt RCA players to TS inputs | Unbalanced | Verify channel mapping (L/R). |
| 12 | 2× RCA → 2× RCA | 2× RCA | Home audio: CD, DVD, receivers | Unbalanced | Use for short distances only. |
🧾 Conclusion
This guide covered everything from basic instrument cables (1/4″ TS, RCA) to professional alternatives like balanced XLR and its variations. With the diagrams and tips you now know each cable’s purpose, correct wiring and precautions to avoid noise and failures.
If you want to learn how to wire Neutrik combo connectors (XLR + 1/4″ jack) used in many consoles and panels, check this related guide: How to Wiring Neutrik Combined Connector.
💬 Which of these cables do you use most often?
Leave a comment below and share your experience — it can help other readers building their own cables!
✨ Our Gratitude and Next Steps
We sincerely hope this guide has been useful and enriching for your projects! Thank you for dedicating your time to this content.
Your Feedback is Invaluable:
Have any questions, suggestions, or corrections? Feel free to share them in the comments below! Your contribution helps us refine this content for the entire ElCircuits community.
If you found this guide helpful, spread the knowledge!
🔗 Share This Guide
Best regards,
The ElCircuits Team ⚡

 Português
Português Español
Español


