Build a HI-FI 14W Audio Amplifier with TDA2030 – DIY PCB Project

Hello, electronics enthusiasts and lovers of good sound!
Today we’re going to dive into a classic project that never goes out of style: a 14W Hi-Fi audio amplifier using the famous TDA2030 integrated circuit. The great advantage of this project is its versatility, as it was designed to work with a 12V symmetrical power supply, making it perfect to be powered by a simple supply or even by batteries in your portable projects.
The TDA2030 is a monolithic integrated circuit in a Pentawatt® package, specifically designed to function as a low-frequency Class AB audio amplifier. It is known for its robustness and sound quality, delivering 14W of power (with d=0.5%) over a 4Ω load with 14V supply. With a symmetrical supply of ±14V, it guarantees 12W in 4Ω and 8W in 8Ω.
Getting to Know the Heart of the Project: The TDA2030 IC
Before we get our hands dirty, let’s understand what makes the TDA2030 such a popular choice. In Figure 2, we have the pinout of this IC. It is designed to provide high output current and, most importantly, an extremely low harmonic and crossover distortion, which results in that clean and clear sound we so appreciate.

In addition to sound quality, the TDA2030 incorporates a sophisticated short-circuit protection system and a mechanism that automatically limits power dissipation. This keeps the output transistors operating within their Safe Operating Area (SOA), even under adverse conditions. A conventional thermal shutdown system is also included, protecting the IC against overheating.
Main Features of the TDA2030
- Wide supply voltage range (up to 36V total)
- Works with single or symmetrical power supply
- Short-circuit protection to ground
- Thermal overload protection (thermal shutdown)
- Low distortion
🔥 Intelligent Short-Circuit Protection
The TDA2030 has a unique circuit that limits the current of the output transistors. The maximum output current is a function of the collector-emitter voltage, which ensures that the transistors always operate within their safe area. Think of it as a “bodyguard” for your amplifier, which prevents damage in case of an accident, such as a wire touching the chassis. This function is more than a simple current limiter; it limits peak power, protecting the IC much more effectively.
🌡️ Thermal Shutdown: The Secret to Durability
The inclusion of a thermal limiting circuit offers crucial advantages for the longevity of your amplifier:
- Output overloads (even if permanent) or high ambient temperatures are easily supported, as the junction temperature (Tj) never exceeds 150°C.
- The heatsink can be sized with a smaller safety factor compared to conventional circuits. There is no risk of damage to the IC due to overheating. If the junction temperature reaches 150°C, the thermal shutdown system simply reduces power dissipation and current consumption, protecting the component.
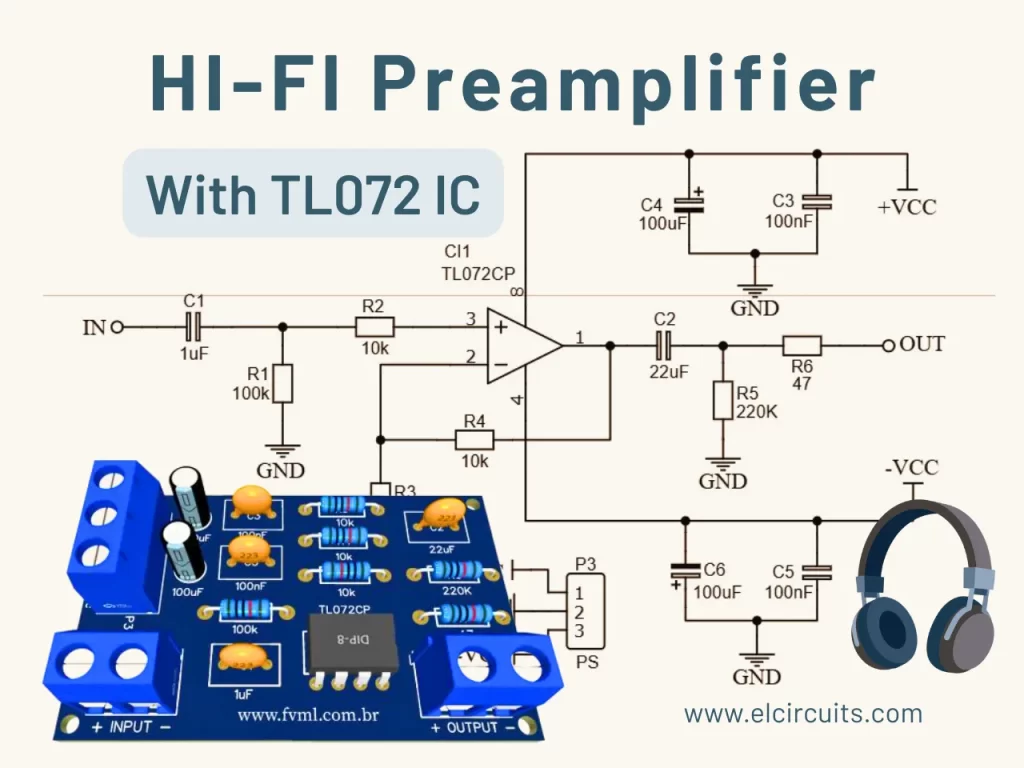
🔌 Schematic Diagram: The Anatomy of the Amplifier
The schematic circuit, shown in Figure 3, is the translation of our project into the language of electronics. It’s a quite simple design, which can be easily assembled even by those who are taking their first steps in circuit assembly. Let’s analyze the main blocks:
- Audio Input: The audio signal enters through connector P1 and passes through potentiometer RP1, which controls the volume.
- Input Stage: Capacitor C1 couples the audio signal to the non-inverting pin (1) of the TDA2030, blocking any DC component. Resistors R1 and R2 establish the correct bias for operation with a single supply.
- Amplification Stage: The heart of the circuit, the TDA2030 (U1), amplifies the signal. The feedback network formed by R3, R4, and R5 defines the amplifier’s gain.
- Output Stage: The amplified signal exits from pin 4, passes through capacitor C4 (which removes any DC component), and is delivered to the speaker through connector P3. Resistor R6 in series with the output helps to stabilize the amplifier with reactive loads.
- Power Supply: The 12V supply is connected to P2. Diodes D1 and D2 are protection diodes, and capacitors C3, C5, and C7 act as filters to ensure a clean and stable voltage for the IC.

🔗 Related Content
If you liked this project, you might also be interested in these
other articles:
-
170W AB Class Bridge Mode Amplifier using TDA7294 IC + PCB
-
HI-FI 120W RMS Amplifier Circuit using LM4780 IC + PCB
-
24W Stereo Hi-Fi Audio Amplifier using TDA2616 + PCB
-
68W Hi-Fi Audio Power Amplifier using LM3886T IC + PCB
-
4 x 50W High Power Amplifier, 14.4V – IC TDA7563A + PCB
-
320W Power Audio Amplifier, Powered with 14.4V – 2Ω with IC
TDA7560 + PCB
-
100W RMS Audio Amplifier IC TDA7294 + PCB
-
200W RMS Stereo Power Amplifier with IC STK4231II + PCB
If you liked this project, you might also be interested in these other articles:
- 170W AB Class Bridge Mode Amplifier using TDA7294 IC + PCB
- HI-FI 120W RMS Amplifier Circuit using LM4780 IC + PCB
- 24W Stereo Hi-Fi Audio Amplifier using TDA2616 + PCB
- 68W Hi-Fi Audio Power Amplifier using LM3886T IC + PCB
- 4 x 50W High Power Amplifier, 14.4V – IC TDA7563A + PCB
- 320W Power Audio Amplifier, Powered with 14.4V – 2Ω with IC TDA7560 + PCB
- 100W RMS Audio Amplifier IC TDA7294 + PCB
- 200W RMS Stereo Power Amplifier with IC STK4231II + PCB
🧾 Bill of Materials: What You’ll Need
Here is the list of materials to assemble this amplifier. Separating everything before starting is always a good practice!
- Semiconductors
- U1 ……………… TDA2030 Integrated Circuit
- D1, D2 ……….. 1N4007 Silicon Diode
- Resistors (1/4W, 5% tolerance, unless specified)
- R1, R2, R3 ….. 100KΩ (brown, black, yellow, gold)
- R4 ……………… 4K7Ω (yellow, violet, red, gold)
- R5 ……………… 150KΩ (brown, green, yellow, gold)
- R6 ……………… 1Ω / 1W (brown, black, gold, gold)
- RP1 …………… 22KΩ (logarithmic) Potentiometer
- Capacitors
- C1 …………….. 2.2µF / 35V Electrolytic
- C2 …………….. 22µF / 35V Electrolytic
- C3 …………….. 1000µF / 35V Electrolytic
- C4 …………….. 2µF / 35V Electrolytic (non-polarized if possible)
- C5 …………….. 100nF (0.1µF) Polyester or Ceramic
- C6……………… 220nF (0.22µF) Polyester or Ceramic
- C7 …………….. 2200µF / 35V Electrolytic
- Miscellaneous
- P1, P2, P3 … 2-Pin Screw Connector (5mm)
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
- Heatsink for the TDA2030
- Enclosure for assembly, wires, etc.
🖨️ Printed Circuit Board (PCB) – Download
To make your life easier and ensure a professional result, we have prepared the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) files. In Figure 4, you can see a preview of the board. The files are available in GERBER, PDF, and PNG formats, covering all your needs:
- GERBER Files: Perfect for sending to a professional PCB manufacturer.
- PDF File: Ideal for printing on transfer paper for the DIY method.
- PNG File: A high-resolution image for visual reference.

📥 Download Project Files (Direct Link):
Click the link below to access the folder with all files: GERBER, PDF and PNG
🤔 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
We’ve compiled some of the most common questions about this project to ensure your experience is the best possible. Check it out!
Can I use a power supply higher than 12V to get more power? 🔽
Yes, the TDA2030 accepts higher voltages. For a symmetrical supply, you can use up to ±18V (total of 36V), which will increase the output power. However, remember that the maximum voltage of the electrolytic capacitors (C1, C2, C3, C4, C7) must be higher than that of the supply (e.g., 50V for ±18V supply). Additionally, the heatsink will need to be larger to dissipate the extra heat.
What is the real power I can expect with a 12V supply? 🔽
With a 12V supply and a 4Ω speaker, you can reliably expect about 8W to 10W of RMS power. The 14W are typically achieved with a slightly higher supply voltage (14V). Still, 10W is more than enough for medium-sized environments and offers clean audio with impressive volume.
Is the use of a heatsink on the TDA2030 mandatory? 🔽
Yes, it is absolutely mandatory. Without an adequate heatsink, the IC will overheat quickly and the thermal protection system will shut it down. In extreme cases, the IC can be permanently damaged. The size of the heatsink depends on the supply voltage and the speaker impedance.
Can I replace the TDA2030 with a TDA2050 for more power? 🔽
Although the pinouts are similar, it is not a direct “drop-in” replacement. The TDA2050 is designed for higher voltages and requires adjustments in the values of the components that define the gain and stability (mainly the resistors and capacitors around pin 2). Using the TDA2030 in the TDA2050 circuit (or vice-versa) can lead to poor performance or even damage the component.
What is the difference between a linear and a logarithmic potentiometer for volume control? 🔽
For volume control, a logarithmic (log) potentiometer is always the best choice. Our ears perceive volume logarithmically, and a potentiometer of this type offers a more natural and progressive volume control. A linear potentiometer would cause most of the volume variation to occur at the beginning of its rotation.
✨ Our Gratitude and Next Steps
We sincerely hope this guide has been useful and enriching for your projects! Thank you for dedicating your time to this content.
Your Feedback is Invaluable:
Have any questions, suggestions, or corrections? Feel free to share them in the comments below! Your contribution helps us refine this content for the entire ElCircuits community.
If you found this guide helpful, spread the knowledge!
🔗 Share This GuideBest regards,
The ElCircuits Team ⚡
 Português
Português Español
Español