Welcome to Lesson 9 - Basic Arduino Course
What is Array?
There are arrays of variables like "char", "int", "boolean", "float" and so on. This means that an array can be variables of any type mentioned above.
An array, or vector, for example, is a collection of variables of a specific type, which may even use the same nomenclature, but which will be distinguished by an indexed number.
Hardware Required
- Arduino Board
- 5 - LEDs
- 5 - 250 ohms resistor - (brown, green, brown, gold)
- Jumper Wires
- Protoboard (optional)
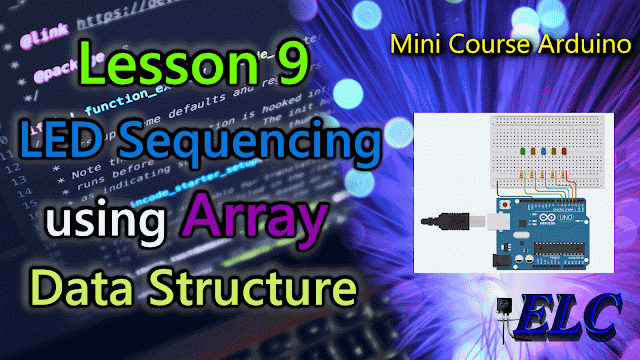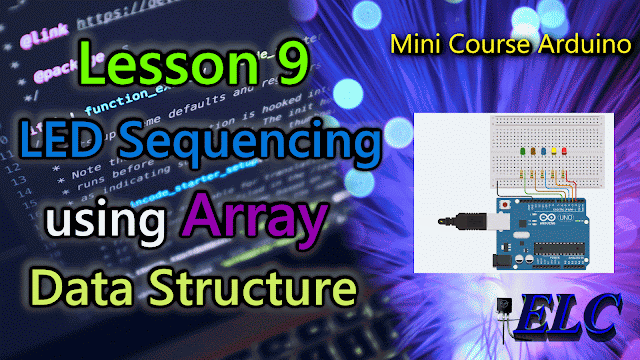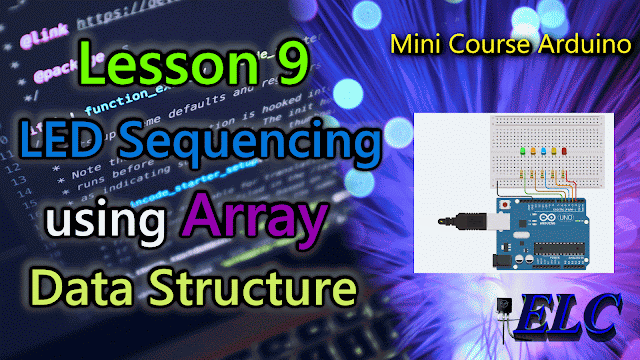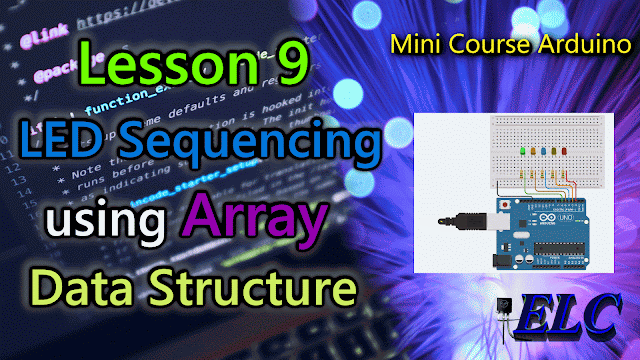
The Circuit Connections
 |
| Fig. 2 - LED Sequencing using Array Data Structure - tinkercad.com |
The Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | // Arduino: Lesson 9 - LED Sequencing using Array Data Structure const int Led1 = 2; // Select the output LED1 PIN const int Led2 = 3; // Select the output LED2 PIN const int Led3 = 4; // Select the output LED3 PIN const int Led4 = 5; // Select the output LED4 PIN const int Led5 = 6; // Select the output LED5 PIN void setup() { // This function is called once when the program starts pinMode(Led1, OUTPUT); // Initialize digital pin LED1 as an output. pinMode(Led2, OUTPUT); // Initialize digital pin LED2 as an output. pinMode(Led3, OUTPUT); // Initialize digital pin LED3 as an output. pinMode(Led4, OUTPUT); // Initialize digital pin LED4 as an output. pinMode(Led5, OUTPUT); // Initialize digital pin LED5 as an output. } void loop() { // The loop function runs over and over again as long as the Arduino has power. // Turn ON each LED sequence in order digitalWrite(Led1, HIGH); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) digitalWrite(Led2, HIGH); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) digitalWrite(Led3, HIGH); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) digitalWrite(Led4, HIGH); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) digitalWrite(Led5, HIGH); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) // Turn OFF each LED sequence in order digitalWrite(Led1, LOW); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) digitalWrite(Led2, LOW); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) digitalWrite(Led3, LOW); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) digitalWrite(Led4, LOW); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) digitalWrite(Led5, LOW); delay(150); // Wait for 150 millisecond(s) } //------------------------------------- www.elcircuits.com -------------------------------------------- |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | // Arduino: Lesson 9 - LED Sequencing using Array Data Structure const int Leds = 5; //Number of LEDs in the circuit const int PinLeds[Leds] = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; //LEDs connected to pins 2 to 6 void setup() { // This function is called once when the program starts for (int i = 0; i < Leds; i++) { // Go through each of the elements in our array pinMode(PinLeds[i], OUTPUT); // And set them as OUTPUT } } void loop() { // The loop function runs over and over again as long as the Arduino has power. for (int i = 0; i < Leds; i++) { // Go through each of the Leds elements in our array digitalWrite(PinLeds[i], HIGH); // And set each of the PinLeds in HIGH level delay(150); // Wait 150 millis seconds, and back to structure For } for (int i = 0; i < Leds; i++) { // Go through each of the Leds elements in our array digitalWrite(PinLeds[i], LOW); // And set each of the PinLeds in LOW level delay(150); // Wait 150 millis seconds, and back to structure For } } //------------------------------------- www.elcircuits.com -------------------------------------------- |
- In Line 3, we declared the number of LEDs in the circuit.
- In Line 4, We are using an Array to index each pin of the LEDs in the corresponding Arduino Ports.
1 2 3 4 5 ... | // Arduino: Lesson 9 - LED Sequencing using Array Data Structure const int Leds = 5; //Number of LEDs in the circuit const int PinLeds[Leds] = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; //LEDs connected to pins 2 to 6 //------------------------------------- www.elcircuits.com -------------------------------------------- |
- In Line 6, we enter the void setup() function. This function is read only once when the Arduino is started.
- In Line 7, we enter in the FOR structure control, to access each Leds element.
- in Line 8, we set each PinLeds as OUTPUT, through each elements in ou array.
1 ... 6 7 8 9 10 ... | // Arduino: Lesson 9 - LED Sequencing using Array Data Structure void setup() { // This function is called once when the program starts for (int i = 0; i < Leds; i++) { // Go through each of the elements in our array pinMode(PinLeds[i], OUTPUT); // And set them as OUTPUT } } //------------------------------------- www.elcircuits.com -------------------------------------------- |
- n Line 11, we enter in the loop() function does precisely what its name suggests, and loops consecutively.
- In Line 12, we enter in the For structure control, to go through each of the Leds elements in our array.
- In Line 13, we continue in the For structure control, and set each of the PinLeds in HIGH level, turn on Led by Led.
- In Line 14, we enter in the delay function, to wait 150 millis seconds, and back to structure For while it is true.
- In Line 16, we enter in the For structure control, to go through each of the Leds elements in our array.
- In Line 17, we continue in the For structure control, and set each of the PinLeds in LOW level, turn off Led by Led.
- In Line 18, we enter in the delay function, to wait 150 millis seconds, and back to structure For while it is true.
1 ... 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | // Arduino: Lesson 9 - LED Sequencing using Array Data Structure void loop() { // The loop function runs over and over again as long as the Arduino has power. for (int i = 0; i < Leds; i++) { // Go through each of the Leds elements in our array digitalWrite(PinLeds[i], HIGH); // And set each of the PinLeds in HIGH level delay(150); // Wait 150 millis seconds, and back to structure For } for (int i = 0; i < Leds; i++) { // Go through each of the Leds elements in our array digitalWrite(PinLeds[i], LOW); // And set each of the PinLeds in LOW level delay(150); // Wait 150 millis seconds, and back to structure For } } //------------------------------------- www.elcircuits.com -------------------------------------------- |
Next Lesson
- Arduino: Lesson 10 - How to Read Temperature and Humidity with Arduino, Using the DHT11 Sensor
- Arduino: Lesson 10 - How to Read Temperature and Humidity with Arduino, Using the DHT11 Sensor
Previous Lesson
If you have any questions, suggestions or corrections, please leave them in the comments and we will answer them soon.
Subscribe to our blog!!! Click here - elcircuits.com!!!
My Best Regards!!!
If you have any questions, suggestions or corrections, please leave them in the comments and we will answer them soon.
Subscribe to our blog!!! Click here - elcircuits.com!!!
My Best Regards!!!