Upgrading Your Applications Using Windows Package Manager (winget) Command on Windows
In today's fast-paced technological landscape, staying up-to-date with the latest software versions is paramount for ensuring optimal performance, security, and access to new features.
With the introduction of the Windows Package Manager (winget) command, Microsoft has streamlined the process of updating and managing applications on Windows systems.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the steps of upgrading your applications using the powerful winget command, ensuring that you harness the full potential of your software ecosystem.
Understanding the Importance of Application Updates
Regularly updating your applications is akin to servicing your car – it keeps things running smoothly and guards against potential vulnerabilities. Outdated software can expose your system to security risks, performance bottlenecks, and compatibility issues.
By proactively upgrading your applications, you not only enjoy the latest features but also maintain a secure and efficient computing environment.
You may be interested in:
Introducing Windows Package Manager (winget)
The Windows Package Manager, known as winget, is a command-line tool developed by Microsoft to simplify the process of installing, updating, and managing software packages on Windows systems.
With a user-friendly syntax and robust functionality, winget eliminates the need to manually search for updates or visit multiple websites to download software.
How to Install Winget?
Winget is installed by default on Windows 11, however if you are using an older version like Windows 10, you will need to install it manually.
To install Winget manually, follow these steps:
- Open the Start menu and search for:
Windows PowerShell.
- Right-click on the search result and select:
Execute as administrator.
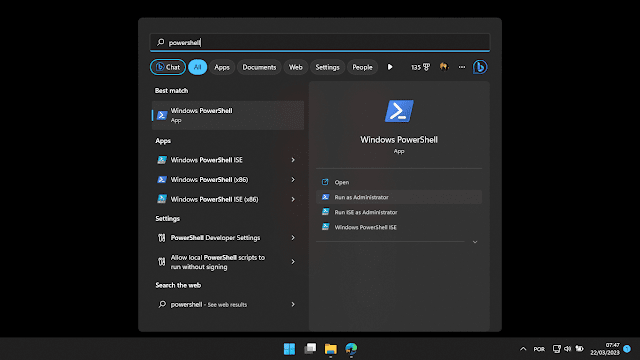 |
| Fig. 2 - Accessing PowerShell windows as administrator |
- Type the following command and press enter:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://aka.ms/winget-cli -OutFile winget-cli.msixbundle
- Type the following command and press enter:
Add-AppPackage -Path winget-cli.msixbundle
Steps to Upgrade Applications Using winget
- Open Command Prompt or PowerShell: Launch the Command Prompt or PowerShell on your Windows system. You can do this by searching for "cmd" or "PowerShell" in the Start menu.
- Check for Updates: Before upgrading any applications, it's a good practice to check for available updates. Use the following command to update the package repository:
- winget update
- List Installed Applications: To view the list of currently installed applications, run the command:
- winget list
This will display a comprehensive list of installed software packages along with their unique identifiers.
How to Update Applications with "Winget Upgrade" Command?
You can be updating all the Applications installed on your Windows quickly and automatically, with a single command. All you have to do is open Command Prompt or PowerShell and type the following command:
- winget upgrade --all
 |
| Fig. 3 - command Winget Upgrade --all cmd |
Upgrade specific Applications
To upgrade a specific application, utilize the command:
- winget upgrade <package_name>
Replace `<package_name>` with the actual name of the package you wish to upgrade. For example:
- winget upgrade GoogleChrome
This will initiate the upgrade process for Google Chrome.
Some Tips for Making the Most of Winget
Here are some tips for getting the most out of Winget:
- Use the "search" command to find new apps to install. For example:
winget search <search term>
- Use the "show" command to see detailed information about an application. For example:
winget show <application name>
- Use the "list" command to see all applications installed on your computer. For example:
winget list
- Use the "uninstall" command to uninstall an application. For example:
winget uninstall <application name>
Advantages of Using winget for Application Upgrades
- Efficiency: winget eliminates the need to visit various websites or application stores to manually download updates. It streamlines the process into a single, command-line interface.
- Automated Updates: By incorporating winget into your workflow, you can schedule automated updates for your applications, ensuring that you never miss a critical upgrade.
- Version Management: With winget, you can easily switch between different versions of a software package, allowing you to test compatibility or revert to a previous version if needed.
- Dependency Handling: winget automatically manages dependencies, ensuring that all required components are installed or updated alongside the main application.
Conclusion
Staying up-to-date with the latest software versions is vital for a seamless and secure computing experience. Windows Package Manager (winget) simplifies the process of upgrading applications on Windows systems, allowing you to effortlessly manage your software ecosystem from the command line.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your applications are always optimized, secure, and equipped with the latest features. Embrace the power of winget and unlock a new level of efficiency in application management.
I hope you enjoyed it!!!
If you have any questions, suggestions or corrections, please leave them in the comments and we will answer them soon.
Subscribe to our blog!!! Click here - elcircuits.com!!!
My Best Regards!!!