Arduino Pro Mini: Complete Pinout and Key Features
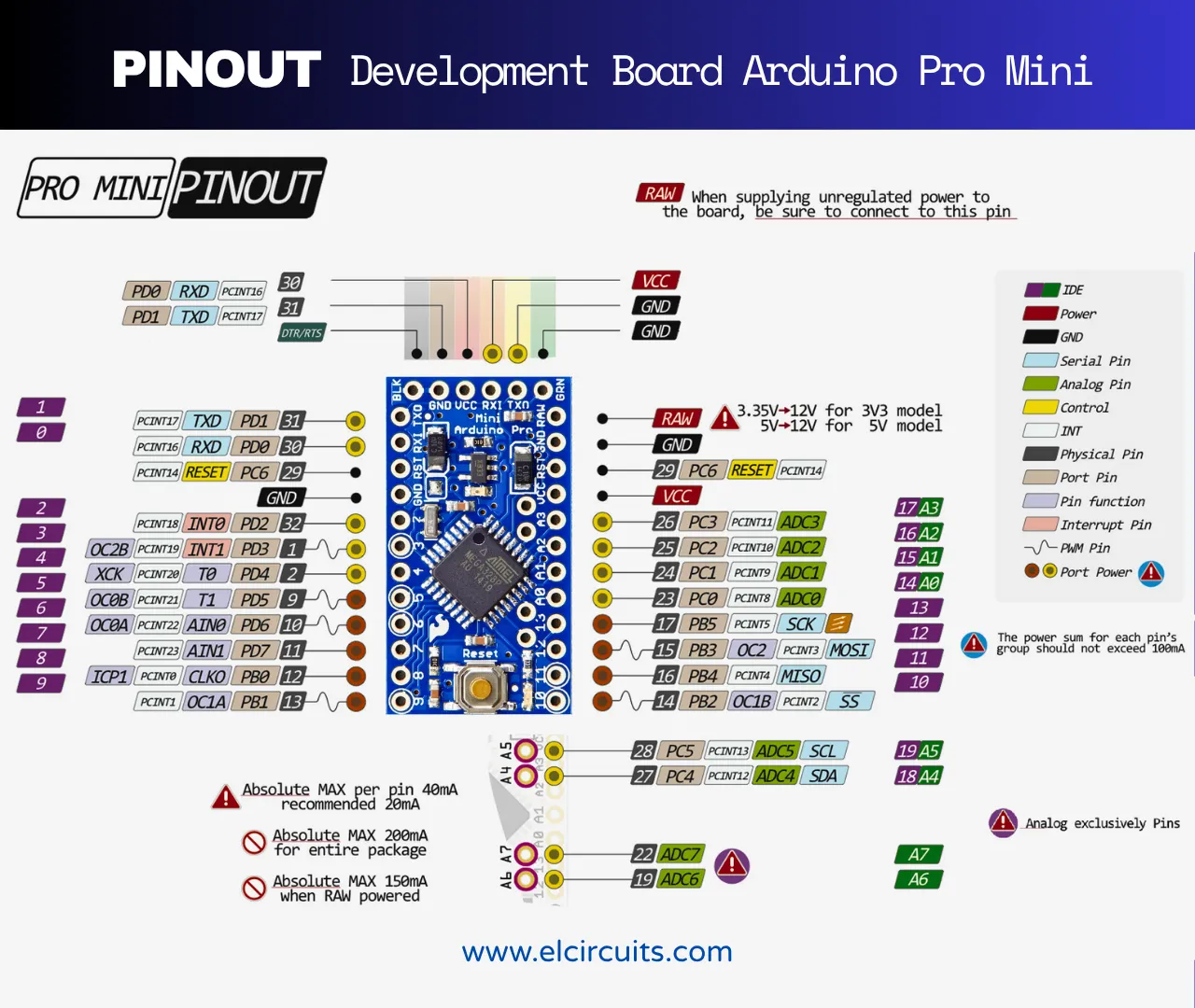
The Arduino Pro Mini is a compact development board based on the ATmega328P microcontroller, designed for applications where space is limited. Its popularity is due to its small size and low power consumption, making it ideal for embedded projects and wearables. Despite its compact size, it maintains the same functionality as other Arduino boards, such as the Uno, but without the edge connectors and without the integrated USB interface.
In this complete guide, we will explore in detail the pinout of the Arduino Pro Mini, analyzing each pin, its functions and limitations. We will cover from the power pins to the communication pins and digital I/O, providing essential information so you can make the most of this board in your projects. We will also discuss the schematic diagram, electrical characteristics and answer the most frequently asked questions about the pinout of this board.
I/O Pin Table (Input/Output)
| Pin on Board | GPIO (Chip) | Main Functions | Critical Notes / Default State |
|---|---|---|---|
| D0 (RX) | PD0 | UART RX | Serial receiver. Used for communication with the computer via USB-Serial converter. |
| D1 (TX) | PD1 | UART TX | Serial transmitter. Used for communication with the computer via USB-Serial converter. |
| D2 | PD2 | Digital, External Interrupt 0 | Can be used as external interrupt. Supports PWM in some configurations. |
| D3 | PD3 | Digital, PWM, External Interrupt 1 | Supports PWM (~) and can be used as external interrupt. |
| D4 | PD4 | Digital | Standard digital pin. Default state: input (high impedance). |
| D5 | PD5 | Digital, PWM | Supports PWM (~). Default frequency: ~490Hz. |
| D6 | PD6 | Digital, PWM | Supports PWM (~). Default frequency: ~490Hz. |
| D7 | PD7 | Digital | Standard digital pin. Default state: input (high impedance). |
| D8 | PB0 | Digital | Standard digital pin. Default state: input (high impedance). |
| D9 | PB1 | Digital, PWM | Supports PWM (~). Default frequency: ~490Hz. |
| D10 | PB2 | Digital, PWM, SS | Supports PWM (~) and is the Slave Select pin for SPI communication. |
| D11 | PB3 | Digital, PWM, MOSI | Supports PWM (~) and is the MOSI pin for SPI communication. |
| D12 | PB4 | Digital, MISO | Is the MISO pin for SPI communication. |
| D13 | PB5 | Digital, SCK, LED | Is the SCK pin for SPI communication and controls the onboard LED. |
| A0 | PC0 | Analog, Digital | Analog input (10-bit). Can be used as digital pin. Resolution: 1024 levels (0-1023). |
| A1 | PC1 | Analog, Digital | Analog input (10-bit). Can be used as digital pin. Resolution: 1024 levels (0-1023). |
| A2 | PC2 | Analog, Digital | Analog input (10-bit). Can be used as digital pin. Resolution: 1024 levels (0-1023). |
| A3 | PC3 | Analog, Digital | Analog input (10-bit). Can be used as digital pin. Resolution: 1024 levels (0-1023). |
| A4 | PC4 | Analog, Digital, SDA | Analog input (10-bit). Can be used as digital pin and SDA for I2C communication. |
| A5 | PC5 | Analog, Digital, SCL | Analog input (10-bit). Can be used as digital pin and SCL for I2C communication. |
| A6 | ADC6 | Analog only | Analog input (10-bit). Cannot be used as digital pin. Resolution: 1024 levels (0-1023). |
| A7 | ADC7 | Analog only | Analog input (10-bit). Cannot be used as digital pin. Resolution: 1024 levels (0-1023). |
Power and Control Pin Table
| Pin on Board | Name | Function | Technical Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAW | VIN | Unregulated power input |
Accepts voltage from 6V to 12V (5V version) or
6V to 9V (3.3V version). Passes through the
voltage regulator.
|
| VCC | VCC | Regulated power output |
Provides 5V (5V version) or 3.3V (3.3V
version) regulated. Can be used to power external components.
|
| GND | GND | Ground | Ground reference pin (0V). There are multiple GND pins on the board. |
| RST | RESET | Reset |
When set to low level, resets the microcontroller. Has a
10kΩ pull-up resistor.
|
| TXO | TX | Serial Transmitter | Connected to pin D1. Used for programming and serial communication via USB-Serial adapter. |
| RXI | RX | Serial Receiver | Connected to pin D0. Used for programming and serial communication via USB-Serial adapter. |
| DTR | DTR | Data Terminal Ready | Used by the USB-Serial adapter to automatically reset the board during programming. |
| GND | GND | Ground | Ground reference pin (0V) for the USB-Serial adapter. |
| AREF | AREF | Analog Reference | Reference voltage for analog inputs (0-5V by default). Can be connected to an external voltage for greater precision. |
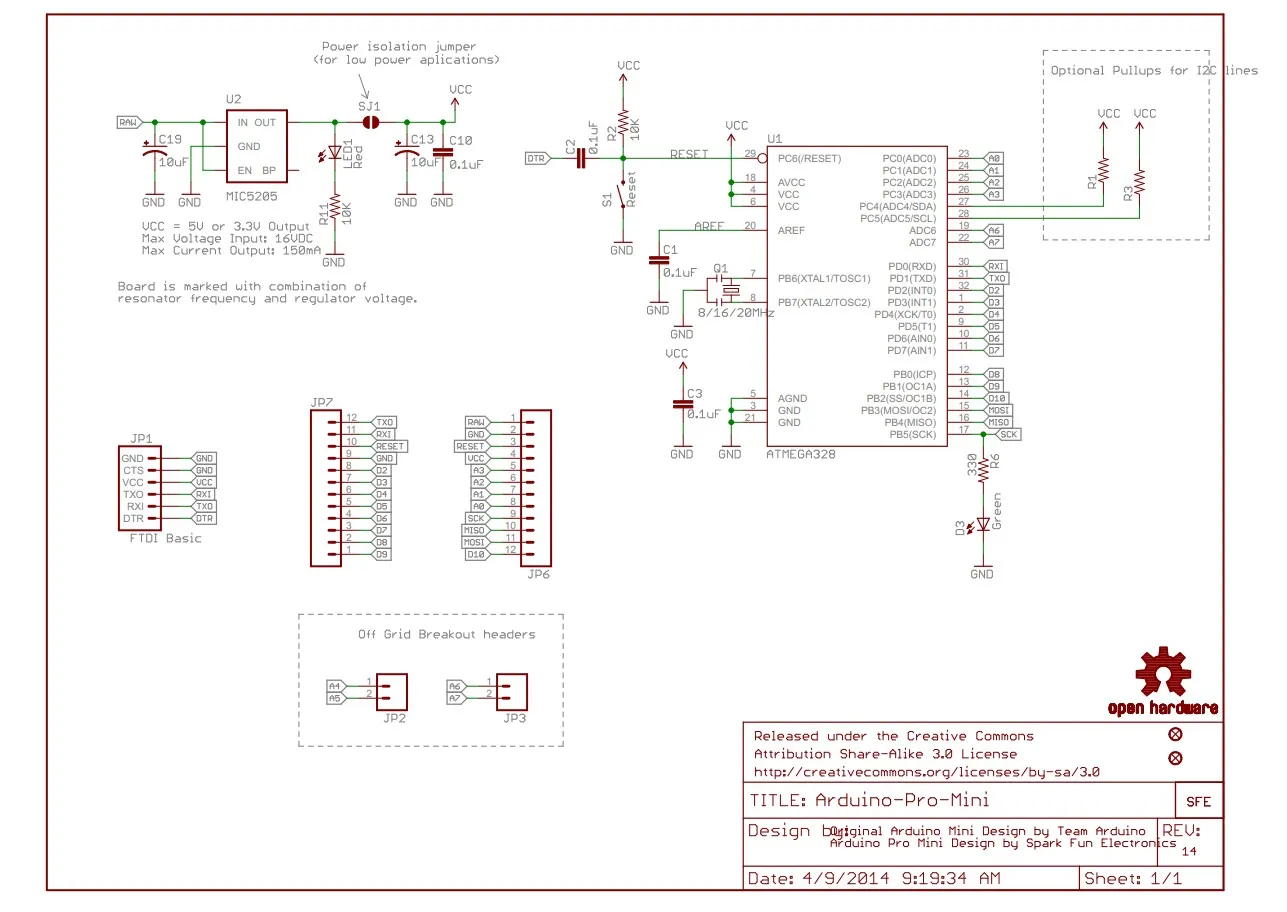
Schematic Diagram
The Arduino Pro Mini schematic diagram shows how the components are connected internally, including the ATmega328P microcontroller, the voltage regulator and the support circuits. This diagram is essential to understand the internal operation of the board and to perform modifications or diagnostics more advanced.
🔗 Related Content
If you liked this project, you might also be interested in these other articles:
- Arduino UNO R3: Pinout and Key Features
- Arduino Mega 2560 R3: Complete Pinout and Key Features
- What is Arduino?
- How to Install Arduino Software (IDE) on Windows - Step by Step!
To view the Arduino Pro Mini schematic, you can access the official Arduino documentation. The document contains complete and up-to-date technical information about the module's hardware. Click here to access the PDF schematic on the official Arduino website.
Summary of Electrical Characteristics and Limitations
-
Microcontroller: ATmega328P operating at
16MHz(5V version) or8MHz(3.3V version). -
Operating Voltage: Available in two versions -
5V(accepts 6-12V on RAW pin) and3.3V(accepts 6-9V on RAW pin). -
Current per I/O Pin: Each digital pin can provide up to
40mA, but the total for all pins should not exceed200mA. -
Flash Memory:
32KB(of which0.5KBare used by the bootloader). -
SRAM Memory:
2KBfor variables during program execution. -
EEPROM Memory:
1KBfor permanent data storage. - USB-Serial Converter: Does not have an integrated converter. An external adapter (such as FTDI FT232RL, CH340G or CP2102) is required for programming and serial communication.
-
Boot Pins: The bootloader is configured to use the pins
RX(D0) andTX(D1) for serial programming.
This Arduino Pro Mini pinout guide was developed to provide a complete and detailed reference for developers and enthusiasts who work with this compact board. Understanding the function of each pin and its limitations is essential to make the most of the Arduino Pro Mini's potential in your projects. Remember that, despite its reduced size, this board offers the same processing capability as other larger Arduino boards, making it ideal for applications where space is a critical factor.
🤔 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
To ensure your project is a success, we've compiled some of the most common questions about this charger. Check it out!
1. How to program the Arduino Pro Mini if it doesn't have a USB port? 🔽
To program the Arduino Pro Mini, you need an external USB-Serial
adapter, such as FTDI FT232RL, CH340G or CP2102. Connect the adapter's
TXO pin to the Pro Mini's RXI, the adapter's
RXI to the Pro Mini's TXO, GND to
GND, and the adapter's DTR to the Pro Mini's
DTR pin. The DTR pin is important as it allows
automatic reset of the board during code upload.
2. What is the difference between the 5V and 3.3V versions of the Arduino Pro Mini? 🔽
The main difference is in the operating voltage and clock frequency.
The 5V version operates with a 16MHz clock and
accepts power from 6V to 12V on the RAW pin.
The 3.3V version operates with an 8MHz clock
and accepts power from 6V to 9V on the RAW
pin. The choice depends on the components you intend to use in your
project, especially sensors and modules that may be
voltage-sensitive.
3. Can I power the Arduino Pro Mini directly through the VCC pin? 🔽
Yes, you can power the Arduino Pro Mini directly through the
VCC pin, but only with the correct regulated voltage (5V
for the 5V version or 3.3V for the 3.3V version). Do not
power the VCC pin with unregulated voltage or with voltage
higher than specified, as this can damage the microcontroller. The
RAW pin should be used when you need to power the board
with a higher voltage that will be regulated internally.
4. How many PWM pins are available on the Arduino Pro Mini? 🔽
The Arduino Pro Mini has 6 PWM pins: D3,
D5, D6, D9, D10 and
D11. These pins can be used to generate pulse width
modulation signals, which are useful for controlling LED brightness, DC
motor speed, or for other applications that require simulated analog
outputs.
5. How to use the A6 and A7 pins that are analog only? 🔽
The A6 and A7 pins are exclusive analog
inputs, which means they cannot be used as digital pins. To use them,
you must read their values using the analogRead() function
with the parameters A6 or A7. They provide
readings from 0 to 1023, corresponding to
0V to 5V (or 0V to
3.3V on the 3.3V version). They are useful when you need
more analog inputs than those available on pins A0 to
A5.
6. Is it possible to use I2C and SPI communication simultaneously on the Arduino Pro Mini? 🔽
Yes, it is possible to use I2C and SPI communication simultaneously on
the Arduino Pro Mini, as they use different pins. I2C communication uses
pins A4 (SDA) and A5 (SCL), while SPI
communication uses pins D10 (SS), D11 (MOSI),
D12 (MISO) and D13 (SCK). However, you must be
careful not to use these pins for other purposes at the same time, and
ensure there are no address or resource conflicts when using multiple
I2C or SPI devices.
✨ Our Gratitude and Next Steps
We sincerely hope this guide has been useful and enriching for your projects! Thank you for dedicating your time to this content.
Your Feedback is Invaluable:
Have any questions, suggestions, or corrections? Feel free to share them in the comments below! Your contribution helps us refine this content for the entire ElCircuits community.
If you found this guide helpful, spread the knowledge!
🔗 Share This GuideBest regards,
The ElCircuits Team ⚡
 Português
Português Español
Español