|
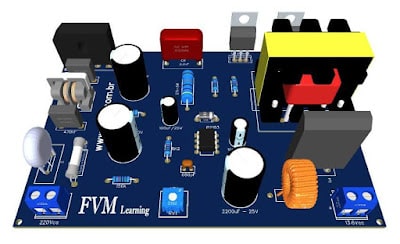
| Mini Switching Power Supply 5V - 25V, 3A with TNY268 and PCB |
Compact 3A Mini Switching Power Supply: Build Your Own 5V-25V Solution with TNY268 and PCB
In this article, we will be discussing a mini switched power supply that provides 5V to 25Vdc output. This power supply is perfect for various electronic devices that require a stable and reliable power supply.
This is a power supply based on the TNY268 Integrated Circuit, which is part of a series of TinySwitch-II circuits: TNY263, TNY264, TNY265, TNY266, TNY267 and TNY268.
For a Flyback-type switched power supply like the one proposed, this IC is ideal, it integrates in its encapsulation the components necessary for it to work:
- PWM Control, Power Mosfets
- Overcurrent Protection
- Over-Temperature Protection
- Self-Feeding System
It does not need auxiliary windings, which makes it a complete IC, with DIP8 encapsulation, with a PWM working frequency of 132kHz and a voltage of up to 700V.
We will dive into the technical specifications, design, and features of this power supply and how it compares to other similar products in the market.
You may be interested in:
- 4A Low-Noise High-Frequency Step-Up DC-DC Converter using MAX1709 with PCB
- Adjustable Power Supply 1.5V to 28V, 7.5 Amps With IC LT1083 + PCB
- Adjustable Power Supply 1.2V to 37V, 6A, Short Circuit Protection with LM317 and TIP36 + PCB
- Adjustable Switching Power Supply 5.1 to 40V, 2.5 Amp using L4960 + PCB
- Symmetrical Adjustable Power Supply 1.25V to 47V 10 Amps with Short Circuit Protection + PCB
- Adjustable Power Supply 1.25v to 57V, 6 Amps with TIP36C + LM317HV + PCB
- Adjustable Power Supply 1.25v to 33V, 3 Amps with LM350 + PCB
- Stabilized Power Supply 13.8V High Current 10 Amps with PCB
Technical Specifications
The mini switched power supply has an input voltage range of 80V to 260V AC, which makes it suitable for use in different parts of the world.
It provides an output voltage that can be regulated between 5V to 25V, with a current of up to 3A, depending on the configuration that we choose.
The power supply also has short-circuit protection and overvoltage protection, ensuring the safety of the connected devices.
Design
The mini switched power supply has a compact design, with dimensions of 55mm x 26mm x 21mm. The power supply is enclosed in a plastic case that protects the circuitry from dust and other environmental factors.
The power supply has a standard WJ2EDGVC-5.08-2P connector, making it easy to connect different electronic devices.
Caution!
"This circuit works directly connected to the electrical network, this is extremely dangerous, any carelessness, or wrong connections, design error, or any other occasion, can lead to irreversible damage.
We are not responsible for any type of occurrence. If you don't have enough experience, don't build this circuit, and if you build it, when testing it, be sure to have the proper protections and be accompanied by someone else."
Features
One of the standout features of this mini switched power supply is its efficiency. It has a high efficiency rating of up to 85%, which means that it wastes less energy as heat compared to other similar products.
This feature is especially important for electronic devices that are battery-powered, as it helps to extend their battery life.
Another feature of this power supply is its low ripple and noise. The power supply has a ripple voltage of less than 50mV, which ensures that the connected devices receive a stable and noise-free power supply.
This is especially important for audio devices, where any noise in the power supply can cause unwanted noise in the audio output.
TNY268 - Pinout and Description
The TNY268 is packaged in a DIP-8B structure for perforated pinouts and an SMD-8B package for SMD.
The package is similar to the well-known IC LM555, with the exception of pin 6 hidden in the TNY268, as we can see in the pinout of Figure 2, below.

|
|
Fig. 2 - Pinout - Pinout TNY268
|
We leave below the description of each pin of the TNY268 Integrated Circuit to facilitate our understanding.
-
DRAIN (D): Power MOSFET drain connection. Provides internal operating
current for start-up and steady-state operation.
-
BYPASS (BP): Connection point for an external 0.1 µF bypass capacitor
for the internally generated 5.8 V supply.
-
ENABLE/UNDERVOLTAGE (EN/UV): This pin has two functions: input enable
and line undervoltage detection. During normal operation, power MOSFET
switching is controlled by this pin. MOSFET switching is terminated
when a current greater than 240 μA is drawn from this pin.
This pin also detects line undervoltage conditions through an external resistor connected to the DC line voltage. If there is no external resistor connected to this pin, TinySwitch-II detects its absence and disables the line undervoltage function.
-
SOURCE (S): Common control circuit, connected internally to the output
MOSFET source.
- SOURCE (HV RTN): MOSFET source connection output for high voltage feedback.
The Switched Power Supply Circuit
The Mini Switched Power Supply Circuit with TNY268 for 5V - 24V, 3A output is a simple yet powerful design, as shown in Figure 3 below.
However, due to the involvement of electricity, it requires careful handling and at least intermediate knowledge of electronics to assemble the circuit.

|
| Fig. 3 - Schematic Diagram Mini Switching Power Supply 5V - 25V, 3A with TNY268 |
The schematic diagram of the Mini Switched Power Supply Circuit is well laid out and easy to understand. It includes a TNY268 controller that regulates the output voltage and current of the power supply.
The circuit has a few essential components such as capacitors, resistors, diodes, and an inductor, which work together to provide stable and efficient power.
Regulate The Output Voltage
The output voltage is adjusted through two parameters in the circuit:
- The D4 diode, which is a 1W Power Zener diode.
- The secondary winding of the transformer.
The Zener Diode
The zener diode D4, is the diode that will adjust the output
voltage, we must configure it as follows,
when the desired voltage is
Xv, the zener diode must have a voltage Xv - 1.
The diode should be 1V lower than the nominal voltage of the power supply, this lower voltage is due to the photocoupler being connected in series with the zener diode, and since it is an “LED” diode, we have the voltage drop on it.
For example:
The Transformer
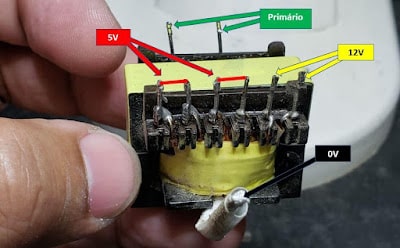
The transformer used in this circuit was a high frequency transformer, often found in PC power supplies, as illustrated in Figure 4 below, a model EE-25 Ferrite transformer.

|
| Fig. 4 EE-25 Ferrite Transformer |
Primary coil winding
The primary will be wound to support a voltage between 85V and 260V, and this will be done by winding 140 turns of 33AWG enamelled wire, or 0.18 mm diameter wire.
Right after winding the primary, place appropriate insulation tape, with electrical and thermal insulation, to insulate the primary from the secondary.
Secondary coil winding
The secondary will be wound according to the desired output voltage, and this will be done in such a way that, for each desired 1V, 1.4 turns of 17AWG enameled wire or 1.15 mm wire are wound.
The calculation for an output voltage of 5V can be achieved using the formula below:
- N = Number of Turns
- V = Desired Voltage
- C = Constant = 1.4
- V = 5V
- C = 1.4
- N = ?
- N = 5 * 1.4
- N = 7 laps
The calculation for an output voltage of 9V:
- V = 9V
- F = 1.4
- N = ?
- N = 9 * 1.4
- N = 12.6 = ~13 Rounds
The calculation for an output voltage of 12V:
- V = 12V
- F = 1.4
- N = ?
- N = 12 * 1.4
- N = 16.8 = ~17 Rounds
The calculation for an output voltage of 24V:
- V = 25V
- F = 1.4
- N = ?
- N = 25 * 1.4
- N = 35 Turns
For 24V output, we have 37 turns to wind in the secondary.
Components list
Semiconductor
- U1 ......... Integrated Circuit TNY268P
- OPT....... TLP181 Opto-Coupler
- D1, D2 ... Diode 1N4007
- D3 ......... Fast Diode FR307
- D4 ......... Zener Diode *See Text
Resistor
- R1 .... Resistor 10Ω / 1W (brown, black, black, gold)
- R2 .... Resistor 200KΩ / 1/4W (red, black, yellow, gold)
- R3 .... Resistor 470Ω / 1/4W (yellow, violet, brown, gold)
Capacitors
- C1 ....... Electrolytic Capacitor 47uF/400V
- C2 ....... Polyester Capacitor 2.2nF
- C3 ....... Polyester Capacitor 100nF
- C4 ....... Electrolytic Capacitor 470uF/35V
Several
- T1 ......... EE-25 Ferrite Transformer
- P1, P2 ... Connector WJ2EDGVC-5.08-2P
- Others... PCI, Wires, Solders, Etc.
Printed Circuit Board - Download
In Figure 5 below, we are making the PCI available in GERBER, PDF and JPEG files, for those who want to create a more optimized assembly, either at home, or if you prefer, at a company that prints the board.
You can download the files for free from a direct link in the Download option below.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mini switched power supply that provides a programable 5V to 25Vdc output is an excellent choice for various electronic devices. Its compact design, high efficiency, and low ripple and noise make it stand out compared to other similar products in the market.
Its safety features, such as short-circuit protection and overvoltage protection, ensure that connected devices are protected from damage. If you are looking for a reliable and efficient power supply for your electronic devices, then this mini switched power supply is a great choice.
You can see the official post by clicking here! fvml.com.br
I hope you enjoyed it!!!
If you have any questions, suggestions or corrections, please leave them in the comments and we will answer them soon.
Subscribe to our blog!!! Click here - elcircuits.com!!!
My Best Regards!!!