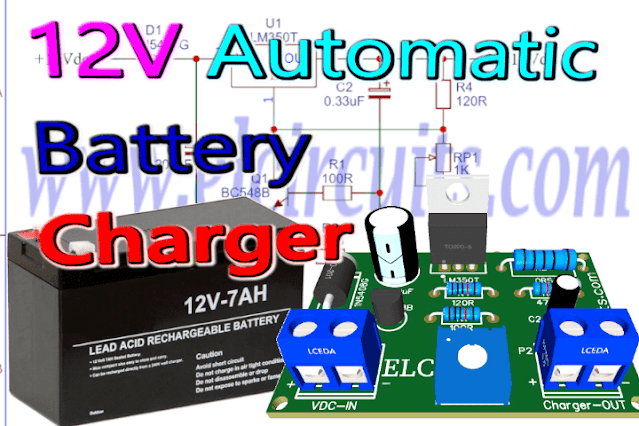
The main advantage of this battery charger circuit is its charging mode, since it has a charge control, so that the battery does not receive voltage when it is not needed, giving more autonomy to the battery and protecting it from overvoltage.
You may be interested in:
What is Lead Acid Battery
It is the first type of rechargeable battery ever created. Compared to modern rechargeable batteries, lead-acid batteries have relatively low energy density.
Lead Acid Battery Charger Method
- Constant current
- Peak charge
- Float charge
The Circuit
Working
Components List
- Semiconductors
- U1 .......... LM350 Voltage Regulator Circuit
- Q1 .......... BC548B NPN Transistor
- D1 .......... 1N5408 Silico Diode
- Resistor
- R1 .......... 100Ω Resistor (brown, black, brown, gold)
- R2 .......... 0.5Ω 5W Resistor (green, black, silver, gold)
- R3 .......... 470Ω Resistor (yellow, violet, brown, gold)
- R4 .......... 120Ω Resistor (brown, red, brown, gold)
- RP1 ........ 1KΩ Potentiometer
- Capacitor
- C1 .......... 2.2uF / 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
- C2 .......... 0.33uF / 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
- Other
- P1, P2 .... 2-pin PCB soldering terminal blocks
- Others .... Printed Circuit Board, Heat Sink, tin, wires, etc.
Printed Circuit Board
In Figure 3, we provide the PCB - Printed Circuit Board, in GERBER, PDF and PNG files. These files are available for free download, on the MEGA server, in a direct link, without any bypass.
All to make it easier for you to do a more optimized assembly, either at home, or with a company that prints the board. You can download the files in the Download option below.
 | |
|
Files to Download, Direct Link:
If you have any questions, suggestions or corrections, please leave them in the comments and we will answer them soon.
Subscribe to our blog!!! Click Here - elcircuits.com!!!
My Best Regards!!!